Offline training
The established approach for designing and training a model for running inference in FTorch is the so-called 'offline' approach, which is described in the following. We are currently working on implementing an alternative online training approach - see the online training user guide page for details.
Workflow
Below we provide a schematic of the offline training workflow, which is broken down into separate tasks below.
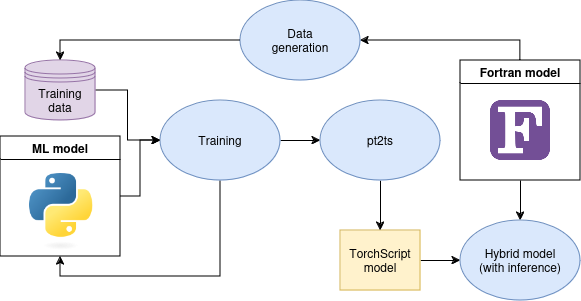
1. Design the ML model in PyTorch
This task is done purely in Python and is not described here. See the PyTorch documentation for information on how to do this.
2. Data generation
This task is done purely in Fortran. Run the Fortran model to generate training data. Depending on how you write the Fortran model output to disk, there may be some work required to get this training data in an appropriate format for later reading into Python.
3. Training
This tasks is done purely in Python. Create a Python script that loads the
training data that was saved to disk, splits it into training and validation
sets, runs an optimizer, and then writes the trained model to a file with .pt
extension. For more information on how to do this, see the
PyTorch documentation.
4. pt2ts
Having written a trained model to a file with .pt extension, use the
pt2ts.py utility Python script to convert it to TorchScript format. A template
pt2ts.py script can be found in the
utils
subdirectory. See the
README
there for more details on how to use the script.
5. Hybrid model
In order to run inference with the trained ML model, you will need to modify
your Fortran model so that it uses FTorch syntax to set up appropriate
torch_tensor and torch_model objects and call the torch_tensor_forward
subroutine to run the inference. For examples of how to do this, see the
examples user guide page.